
The term mathematical coincidence is used when two expressions show a near-equality and cannot be explained through the theories currently available. Here are the three most interesting mathematical coincidences:
The numerical value of the acceleration caused by Earth’s gravitational force lies between 9.74 and 9.87, on the surface of Earth, which is very close to 10. Further, this means that a kilogram mass on the surface of Earth corresponds to roughly 10 Newtons of force exerted on the object, as per Newton’s second law.
This can be touted as a mathematical coincidence, when we observe that the square of pi is close 10. The most preliminary definition of a meter was the length of a pendulum whose half swing had a period equal to one second.
The time period of the full swing of a pendulum is computed by the equation shown below. Going by this definition algebraically, gravitational acceleration measured in meters per second square would be exactly equal to the square of pi.
The second half of 20th century witnessed increased progress in accurately measuring the speed of light, first by cavity resonance techniques and later by laser interferometer techniques. In 1972, using the latter method and the 1960 definition of the metre in terms of a particular spectral line of krypton-86, a group at NBS in Boulder, Colorado determined the speed of light in vacuum to be c = 299,792,456.2±1.1 m/s.
Hence, the widely accepted definition of speed of light is that it is exactly 299,792,458 m/s, very close to 300,000,000 m/s. It also roughly equals to one foot per nanosecond (the actual number is 0.9836 ft/ns).It is purely coincidental, that the meter was originally defined as 1/10,000,000 of the distance between the Earth’s pole and equator along the surface at sea level. Also, Earth’s circumference is equivalent to be about 2/15 of a light-second.
A Kepler triangle is a right triangle with edge lengths in geometric progression. According to some sources, Kepler triangles appear in the design of Egyptian pyramids.The ratio of the edges of a Kepler triangle is linked to the golden ratio ![]() , or approximately 1 : 1.272 : 1.618, where
, or approximately 1 : 1.272 : 1.618, where
Whereas, German mathematician and astronomer Johannes Kepler, constructed the triangle differently, a Kepler’s triangle can be constructed with only straightedge and compass by first creating a golden rectangle.
To understand the coincidence surrounding this theory, take any Kepler triangle with sides ![]() and consider the following:
and consider the following:
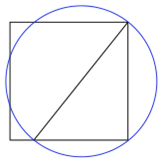
Then the perimeters of the square (![]() ) and the circle (απ℘) coincide up to an error less than 0.1%.
) and the circle (απ℘) coincide up to an error less than 0.1%.
Here is the mathematical coincidence ![]() . The square and the circle cannot have exactly the same perimeter, because if that happens once would be able to solve the classical problem of the quadrature of the circle, which as of now has been touted as impossible. In other words,
. The square and the circle cannot have exactly the same perimeter, because if that happens once would be able to solve the classical problem of the quadrature of the circle, which as of now has been touted as impossible. In other words, ![]() because π is a transcendental number.
because π is a transcendental number.
Featured Image: Linkedin.com